Leave Your Message
-
E-mail
-
Skype
-
Whatsapp
-
Wechat


The rise of smart cities has increased interest in the IoT Street Light Controller System. This technology provides efficient lighting solutions and enhances energy management. Cities can save costs while improving safety for residents.
Implementing an IoT Street Light Controller System can seem challenging. Each city has unique needs and conditions. Factors like weather and traffic patterns affect the system's effectiveness. These variations often lead to unexpected results. Choosing the right components requires careful planning.
A successful IoT Street Light Controller System should integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure. Proper maintenance is crucial to avoid downtime. Regular assessments help identify potential issues. These elements are essential for a reliable system. Ultimately, ongoing reflection and adaptability play a vital role in long-term success.


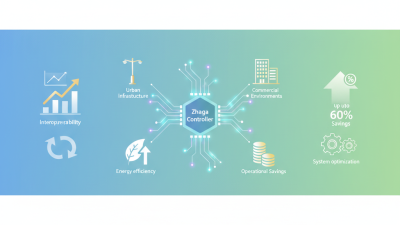
IoT street light controller systems rely on interconnected devices to enhance street lighting efficiency. These systems use sensors to monitor ambient light levels. In urban areas, this technology can significantly reduce energy consumption. According to a recent report from the International Energy Agency, smart lighting can lower street lighting energy use by up to 50%.
But implementing these systems isn’t always straightforward. Many municipalities face challenges in integration. Communication between devices can be inconsistent. A smart city report noted that nearly 40% of cities struggle with compatibility issues among different IoT solutions. This fragmentation can lead to increased costs and inefficiencies. It’s critical for city planners to address these integration challenges early on.
Data management is another area needing attention. IoT street lights generate substantial data. However, improper management can lead to information overload. Cities often lack the infrastructure to analyze this data effectively. A survey by McKinsey showed that only 30% of city officials felt prepared to use IoT-generated data for decision-making. Ensuring that data channels are efficient will enhance performance and guide future investments in smart lighting technology.
An effective IoT street light system should prioritize energy efficiency and adaptability. Smart sensors can detect ambient light levels and adjust illumination accordingly. This helps in saving energy and reducing operational costs. Regular updates are crucial, but integrating them can be problematic. The system must be user-friendly, allowing easy adjustments by city personnel.
Real-time data tracking is essential for maintenance. Systems should monitor bulb performance and alert when replacements are needed. However, not all data is useful; filtering out irrelevant information is important. Security is another critical feature. Vulnerable systems can be targeted, risking public safety. Therefore, strong encryption and secure connections should not be overlooked.
Interconnectivity with traffic systems can enhance functionality. When street lights coordinate with traffic signals, traffic flow improves. Yet, this relies on a reliable network infrastructure. Challenges remain in ensuring signal strength and reducing downtime. An effective IoT street light controller must find a balance. Flexibility and innovation will lead to smarter urban environments.
Smart sensor integration in street lighting systems enhances efficiency significantly. According to a recent industry report, cities utilizing smart street light controllers can reduce energy costs by up to 40%. This impressive figure shows how smart technology can illuminate urban areas sustainably.
Integrating sensors allows for real-time monitoring of light levels and pedestrian traffic. These systems can adjust brightness depending on need, which not only saves energy but also increases safety. However, ensuring proper calibration of these sensors remains a challenge. Overly sensitive devices may lead to unnecessary brightness and wasted energy.
Moreover, there is often a delay in data processing. This lag can hinder the effectiveness of immediate responses needed in emergency situations. Cities must invest in robust data analytics to address these issues. While the potential is massive, the implementation requires ongoing evaluation. Each city's unique characteristics can complicate integration efforts, demanding tailored approaches.
In today's smart cities, effective monitoring of IoT street light systems is essential.
Data analytics enables city managers to gather insights on energy usage and operational efficiency. By analyzing data, they can identify patterns, resulting in better system performance.
One tip for effective analytics is to collect data in real time. This allows for immediate responses to issues as they arise. Consider the impact of system failures on public safety. Delayed reactions can lead to accidents.
Another tip focuses on benchmarking performance. Establish clear metrics to track the efficiency of street lights. Regularly review these metrics for improvements. Unexpected issues might emerge, revealing areas for greater efficiency. This reflection can drive future upgrades in the system.
Incorporating advanced monitoring tools can elevate street light management. However, it is crucial to ensure that the data collected is relevant and actionable. Sometimes, data overload can lead to confusion rather than clarity. Balancing detail with simplicity will enhance overall effectiveness.
In today's smart city initiatives, IoT street light systems are pivotal. However, security and privacy concerns loom large. A recent report indicated that 70% of cities worry about unauthorized access to their IoT networks. Vulnerabilities can expose data and compromise public safety.
Moreover, many IoT street light systems lack robust encryption. Data transmitted without proper security can be intercepted. This is alarming, especially since it involves monitoring public spaces. A report by Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that cybercrime will cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Municipalities need to invest in securing their IoT infrastructures to protect against these threats.
Regular software updates are essential. Yet, only 30% of IoT devices receive timely updates. This negligence can leave systems vulnerable. Transparency in data collection is also critical. Citizens deserve to know how their information is used. Involving the community in discussions about privacy can help build trust and ensure ethical usage.